Create Validator with Custom Authentication
Main Info
|
This is only used when choosing the Custom authentication option when creating a Canton Validator, the alternative is using a with Integrated Keycloak that automates the process as detailed in Create Validator With Integrated Keycloak |
When installing Catalyst is configured Identity Provider that is used to authenticate Catalyst and the validators deployed through it.
This is a brief overview on how to setup Clients and users in your Identity Provider before setting the Validator. For a full description of requirements consult the Canton Validator OICD requirements.
|
The sections on secrets and other configuration on Kubernetes can ignored be as Catalyst creates them. When creating a validator the clients and users need to be setup beforehand. |
Clients
The following clients are used by a Validator node, they need the proper flow allowed in your Identity provider.
|
It is recommended to allow all audiences for the clients when creating the validator, these can be limited after Catalyst generates the URLs and these can be consulted. |
Validator Component |
Open Id Flow |
Fields required by Catalyst |
Validator |
Client Credentials Grant |
Client Id, Client secret |
Canton Name Service |
Authorization Code |
Client Id |
Wallet |
Authorization Code |
Client Id |
Users
A single user is needed to be created before with access to the clients created.
|
This user will be mapped to the main Validator party and will recevie rewards, these can be view from the Wallet. |
1 - Main settings configuration:
At the first step of the new Validator setup wizard, please provide the following information.
-
Name
-
Onboard secret
-
Image tag
-
Image repo
-
Image pull secret
-
Postgres user
-
Postgres password
-
Requested CPU
-
CPU limit
-
Requested memory
-
Memory limit
-
Replicas
More info about these fields
-
Name The identifier or label for the validator node.
-
Onboard secret pass phrase obtained form the super validator in order to join the network.
-
Image tag The specific version or tag of the container image to be used.
-
Image repo The repository where the container image is stored.
-
Image pull secret Credentials required to pull the container image from a private registry. (secret docker-registry)
-
Postgres user Username for the Postgres database used by the validator.
-
Postgres password Password for the Postgres database user.
-
Requested CPU The minimum amount of CPU resources requested for the validator node.
-
CPU limit The maximum amount of CPU resources the validator node is allowed to use.
-
Requested memory The minimum amount of memory requested for the validator node.
-
Memory limit The maximum amount of memory the validator node is allowed to use.
-
Replicas The number of instances of the validator node to run.
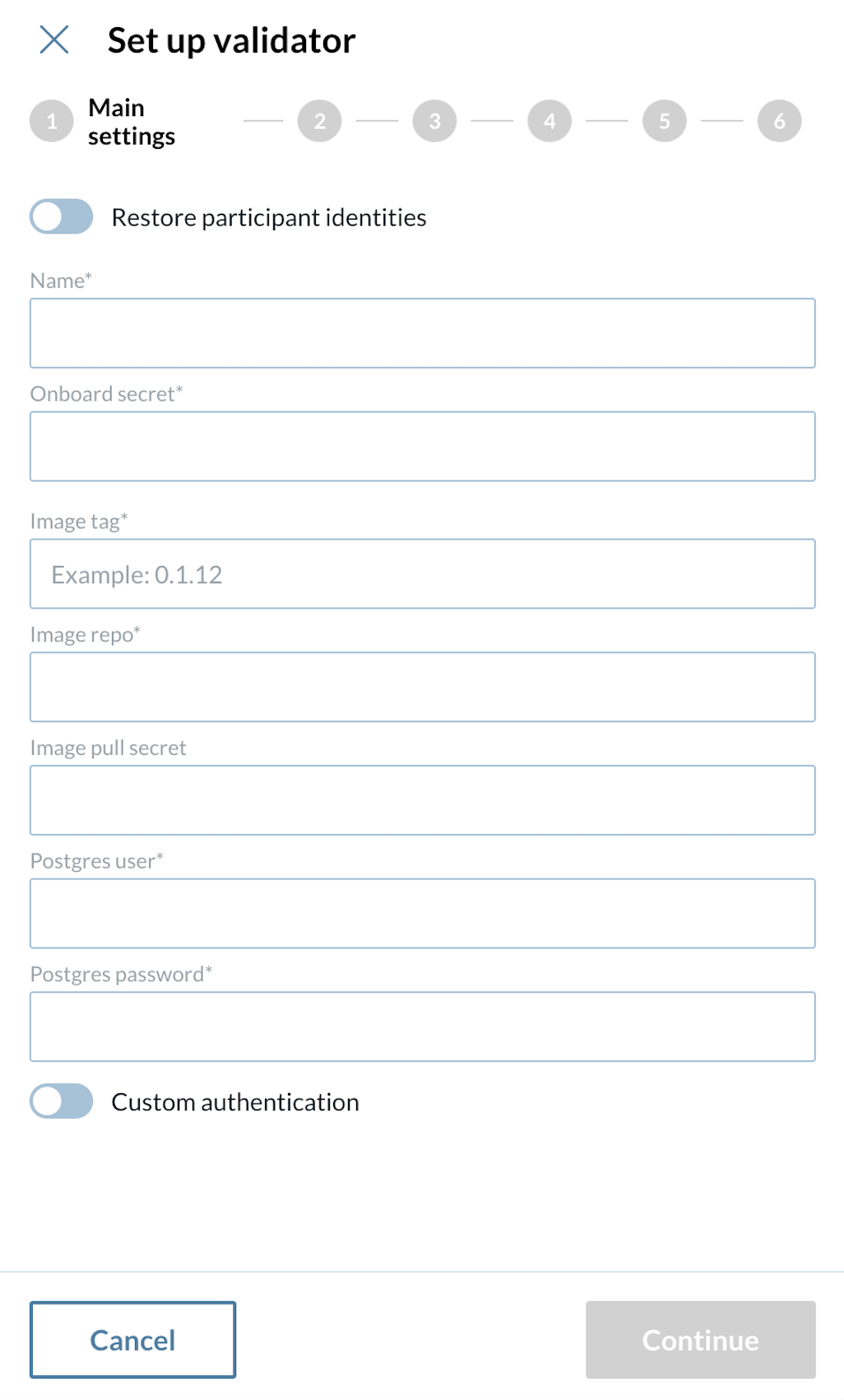
| An onboarding secret should be requested from your sponsoring SV in order to join the network. |
|
Do not forget to set the Custom Authentication flag on as these instructions aim to guide you for a custom indetity provider configuration. If instead you want to follow an integrated Keycloak approach, please refer to the Create Validator With custom identuty provider section |
Now, set the Validator Creation Fields
-
CNS Client Id: Client for the Canton Name Service
-
Wallet Client Id
-
Ledger API Client Id
-
Ledger API Client Secret
-
Ledger API User
-
Wallet User
-
Audience
More info about these fields
-
CNS Client Id: Client for the Canton Name Service
-
Wallet Client Id: Client for Wallet application
-
Ledger API Client Id: Client for Validator
-
Ledger API Client Secret: Secret part of Client Credentials Grant Flow for the Validator client
-
Ledger API User: User of the components described above
-
Wallet User: User that will access the wallet application and receive rewards
-
Audience: Audience claim expected by the clients
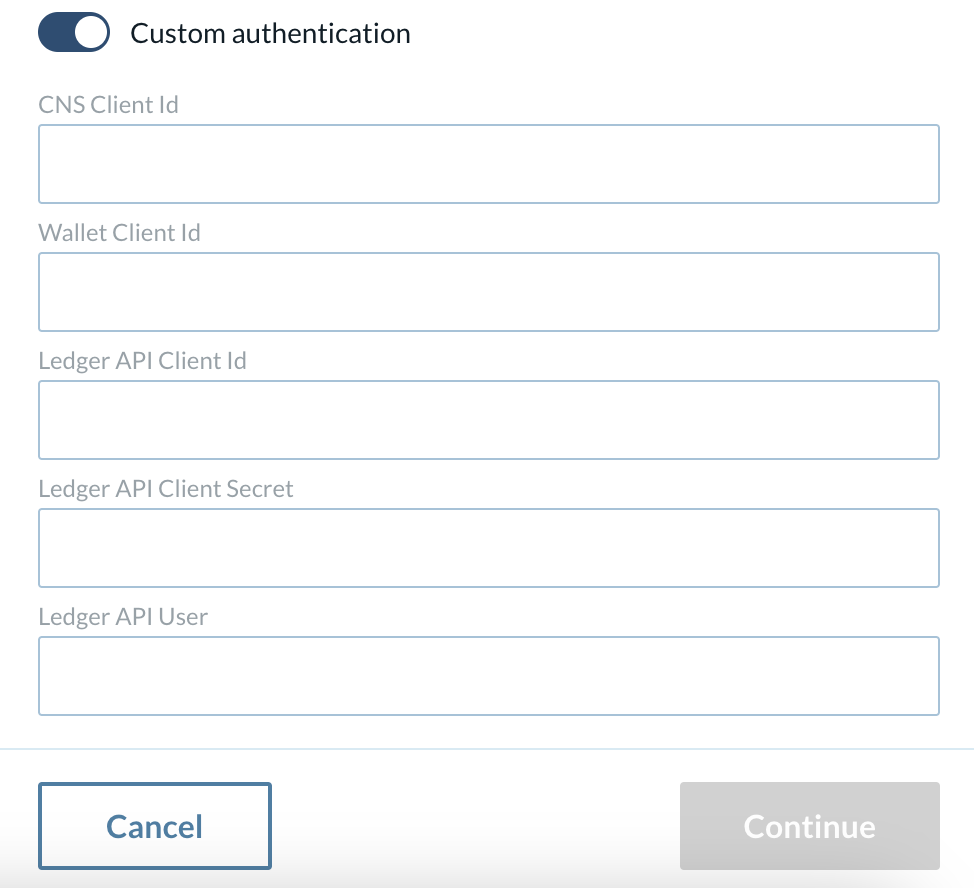
|
The value to set the Ledger API User and Wallet User depends on the Identity provider, the value should be what the Identity Provider puts as the subject field on the JWT token. |
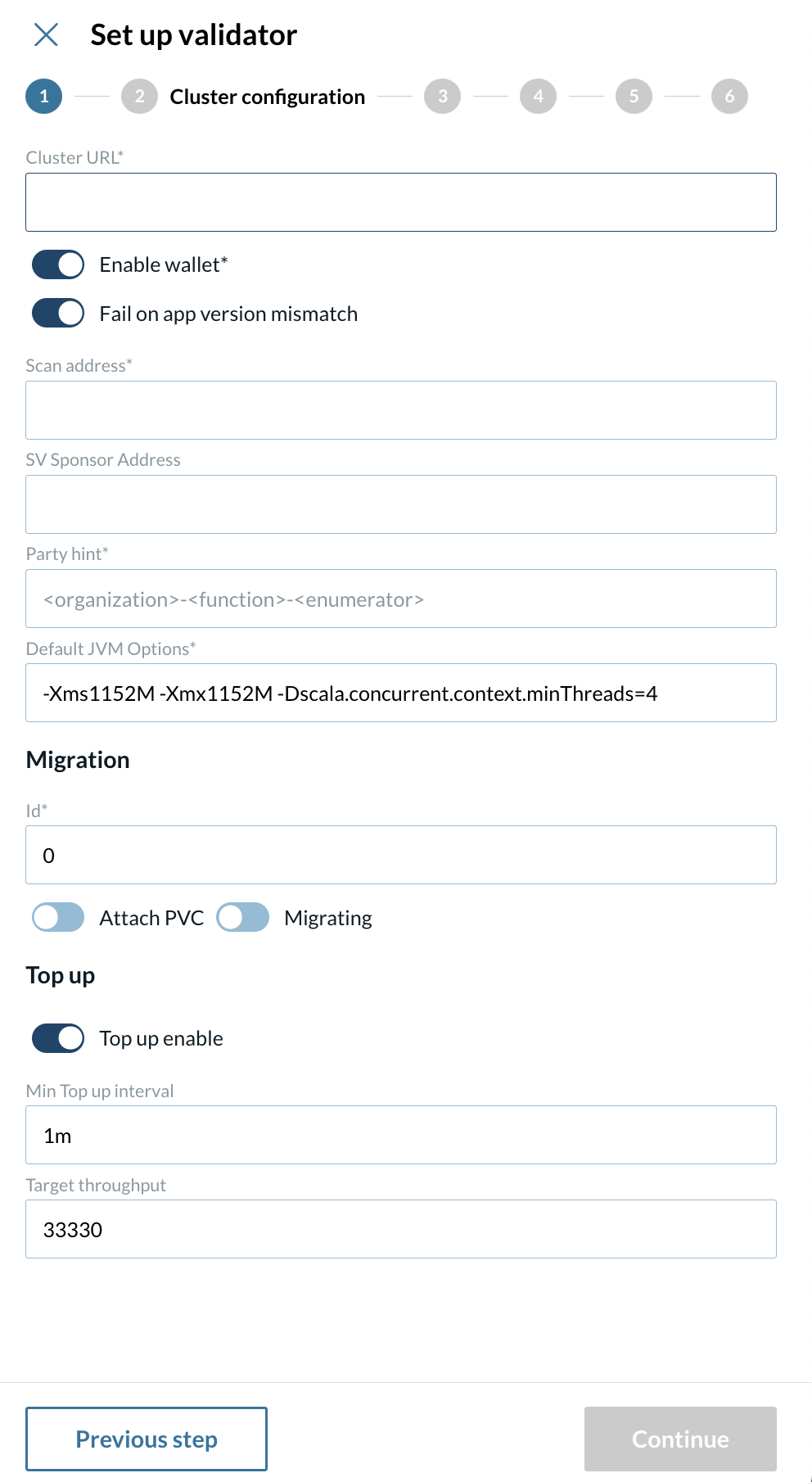
2 - Set up your cluster configuration
At the second step of your validator config, start by inserting the Cluster URL.
2.1 - Enable or disable each of the following fields:
-
Enable wallet
-
Fail on app version mismatch
-
Use sequencer connections from scan
2.2 - Fill in the remaining fields:
-
Cluster URL
-
Enable wallet
-
Fail on app version mismatch
-
Scan address
-
SV Sponsor Address
-
Party hint
-
Default JVM Options
-
Migration
-
Id
-
Attach PVC
-
Migrating
-
-
Top up
-
Enable
-
Top up min interval
-
Target throughput
-
2.3 - Enable or disable:
-
Participant identities dump import
-
Participant identities dump periodic backup
More info about these fields
-
Cluster URL The URL of the Kubernetes cluster where the validator node is deployed. clusterUrl value is used for looking up directory entries in the scan UI.
-
Enable wallet Turn this on to deploy a wallet UI with your validator.
-
Fail on app version mismatch If enabled, the deployment will fail if there is a mismatch between the validator and network application versions.
-
Scan address The address used for scanning and retrieving validator-related data.
-
SV Sponsor Address The URL of the SV app of the super validator sponsoring you. Typically provided by your SV sponsor and starts with "https://sv.sv-N" (N being a number).
-
Party hint Used as a prefix for the Party ID of your validator’s administrator. Must follow the format: <organization>-<function>-<enumerator>, e.g., myCompany-myWallet-1.
-
Default JVM Options Default configuration options for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) running the validator.
-
Migration
-
Id Used to track database migrations. The migration ID starts at 0 for the initial deployment and increments by 1 with each migration.
-
Attach PVC Option to attach a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) for data persistence during migration. Creates a Volume to store migration dumps (recommended).
-
Migrating Set to true when upgrading the validator to trigger the migration process.
-
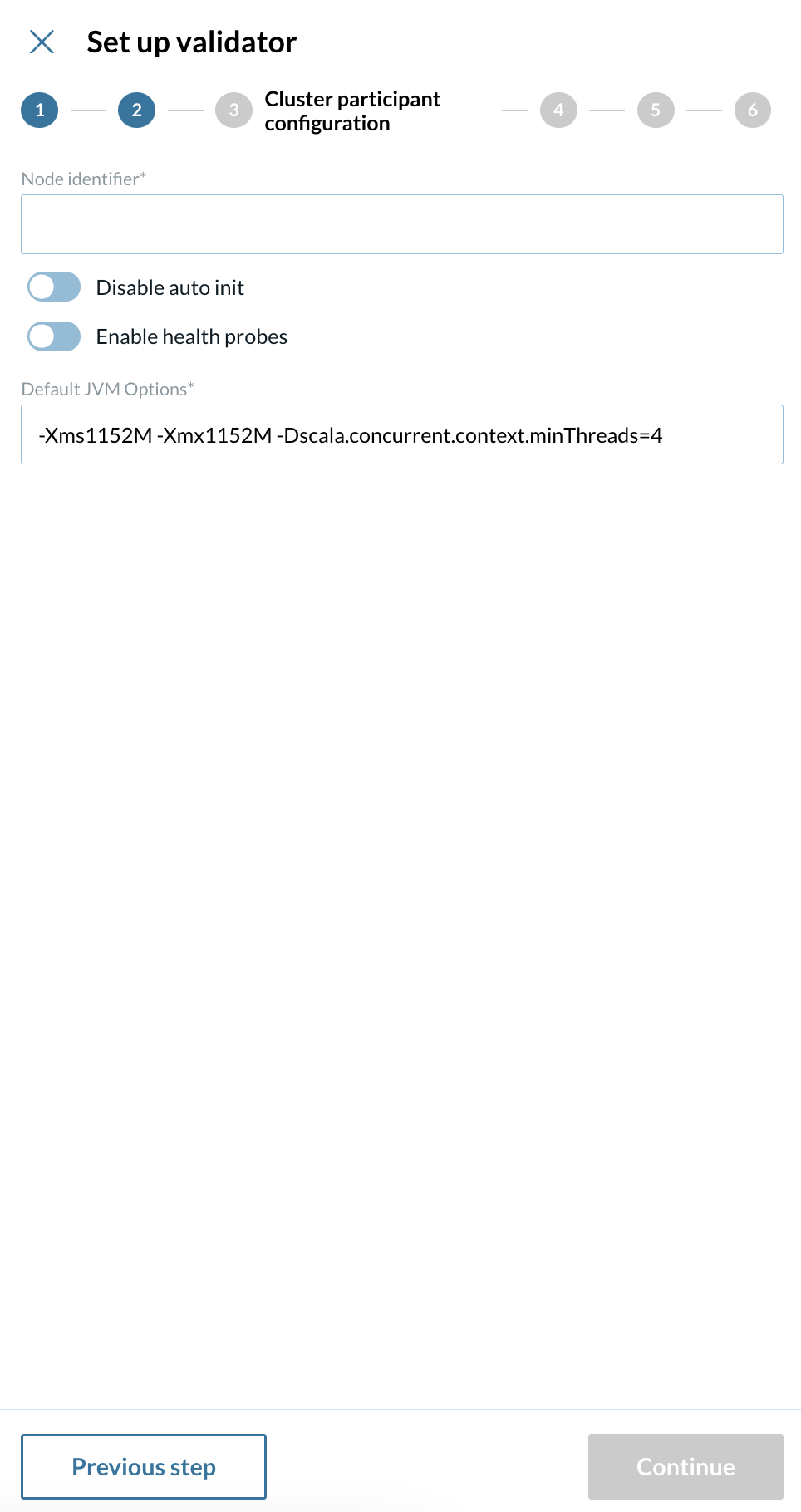
3 - Set up your cluster participant configuration
-
Insert your default JVM configurations
-
Enable or disable
-
Auto init
-
Enable health probes
-
-
Insert your Node Identifier
More info about these fields
-
Node identifier A unique identifier for the validator node within the network.
-
Disable auto init Prevents the validator from automatically starting after deployment, allowing for pre-run actions to be performed before initialization.
-
Enable health probes Turns on health checks to monitor the validator’s status and ensure it is functioning properly.
-
Default JVM Options Default configuration options for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) running the validator.
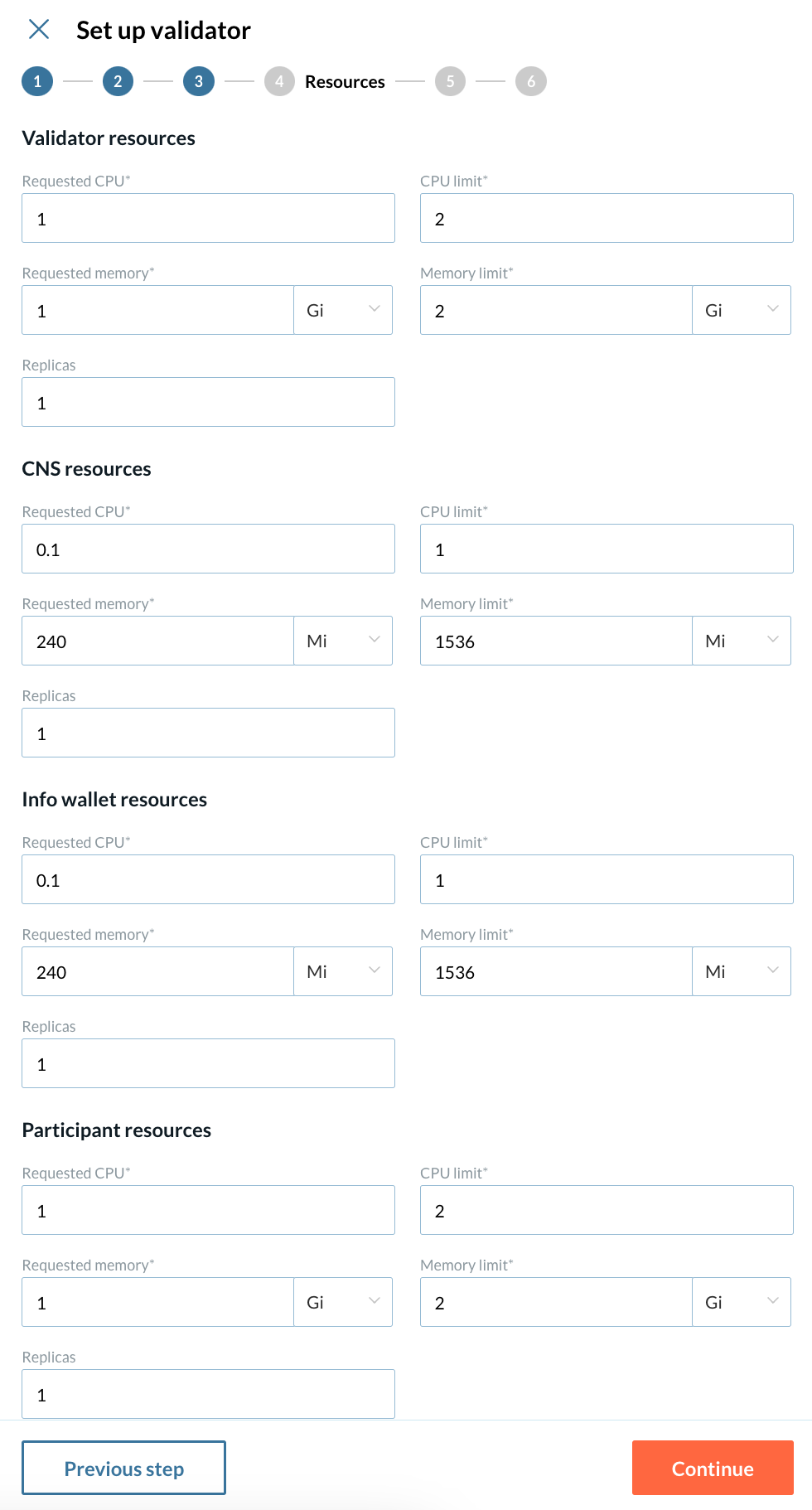
4 - Config Resources
Provide the following information: * Requested CPU * CPU limit * Requested memory * Memory limit * Replicas
More info about these fields
-
Requested CPU The minimum amount of CPU resources requested for the validator node.
-
CPU limit The maximum amount of CPU resources the validator node is allowed to use.
-
Requested memory The minimum amount of memory requested for the validator node.
-
Memory limit The maximum amount of memory the validator node is allowed to use.
-
Replicas The number of instances of the validator node to run.
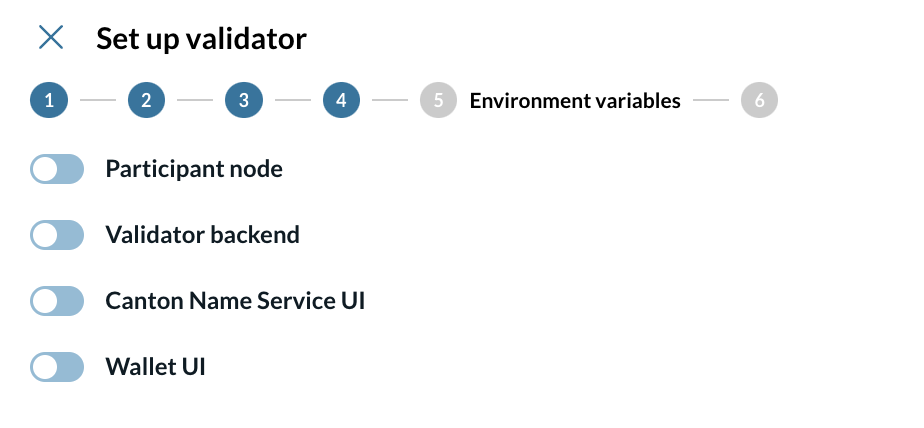
5 - Config environment variables
On this screen, you can override the values of the environment variables created during the wizard configuration for the following components:
-
Participant node
-
Validator backend
-
Canton Name Service UI
-
Wallet UI
More info about these fields
-
Participant node The node that interacts with the Canton ledger on behalf of participants.
-
Validator backend The backend service responsible for validating and processing transactions within the network.
-
Canton Name Service UI The user interface for managing and viewing Canton network names and identifiers.
-
Wallet UI User interface for interacting with the wallet associated with your validator.
|
This is a very specific configuration, if you are not sure about this step, please contact IntellectEU. |